 Tel/WhatsApp
Tel/WhatsApp


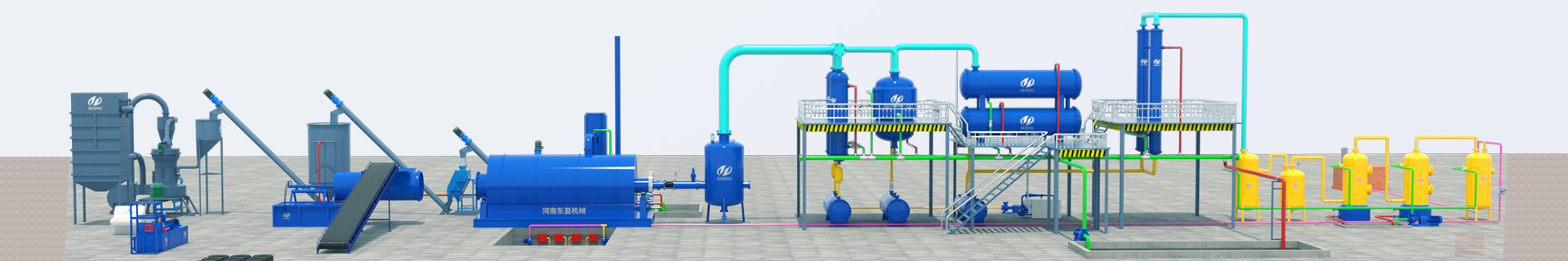
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic materials in the absence of oxygen, typically producing useful products such as fuel oil, syngas, and carbon black. However, in practice, smoke generation is a common issue that can indicate inefficiencies or equipment problems.
Pyrolysis requires an oxygen-free environment to prevent combustion. However, even minor oxygen intrusion can lead to partial combustion of the feedstock, producing smoke. Common sources of oxygen leakage include:
Poor Sealing: Gaskets, flanges, or pipes that are not properly sealed can allow air ingress.
Air Lock Malfunction: In continuous systems, air locks (e.g., screw feeders or rotary valves) that fail to isolate the reactor from ambient air can introduce oxygen.
Solution: Regularly inspect and maintain all seals and air locks. Use high-quality sealing materials and consider installing oxygen sensors to monitor and detect leaks in real-time.
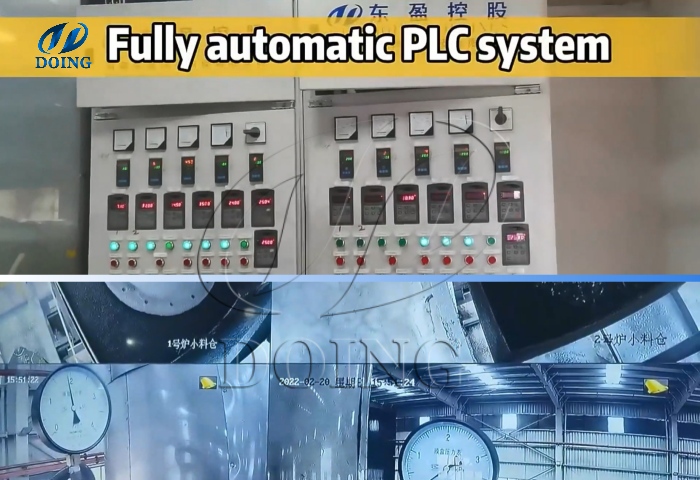
DOING pyrolysis plant fully automatic PLC system
Excessive temperatures or uneven heating can cause incomplete pyrolysis, leading to the formation of volatile compounds that may escape as smoke. Common issues include:
Temperature Fluctuations: Rapid temperature changes can create localized hot spots.
Insufficient Heat Distribution: Poor reactor design or fouling can result in uneven heating.
Solution: Implement precise temperature control systems and ensure uniform heat distribution. Regularly clean and inspect the reactor to prevent fouling.
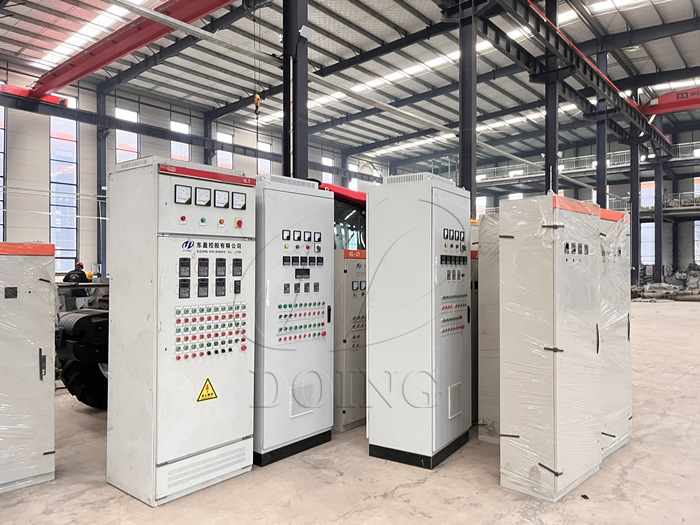

DOING pyrolysis plant electrical control cabinet
The quality of the feedstock directly impacts pyrolysis efficiency. Key factors include:
Moisture Content: High moisture levels generate steam, which can carry particulate matter, forming smoke.
Contaminants: Impurities such as metals, plastics, or non-organic materials can interfere with pyrolysis, leading to incomplete decomposition.
Solution: Pre-treat feedstock to reduce moisture (e.g., drying) and remove contaminants. Use feedstock with consistent properties to ensure stable pyrolysis conditions.
Inefficient condensers or malfunctioning gas cleaning systems can allow volatile compounds to escape as smoke. Common problems include:
Inadequate Cooling: Insufficient cooling capacity prevents complete condensation of gases.
Filter Failure: Clogged or worn-out filters fail to remove particulates and harmful gases.
Solution: Optimize condenser efficiency by increasing cooling capacity or using multiple-stage condensers. Regularly maintain and replace filters, scrubbers, and other gas cleaning components.

DOING waste pyrolysis equipment environmental protection devices
Aging or poorly maintained equipment can lead to oxygen intrusion, overheating, and other issues. For example:
Cracked Reactors: Long-term use can weaken reactor walls, creating leaks.
Worn-Out Components: Valves, seals, and pipes may deteriorate over time.
Solution: Conduct routine inspections and maintenance. Replace worn-out components promptly and consider upgrading to corrosion-resistant materials.
DOING solid waste pyrolysis equipment manufacturer
Smoke production in pyrolysis systems is often a sign of inefficiencies or equipment issues. By addressing oxygen control, temperature management, feedstock quality, and system maintenance, smoke can be minimized or eliminated. At HENAN DOING Group, we specialize in designing and optimizing pyrolysis equipments to ensure high efficiency and environmental compliance. Contact us to learn more about how we can help you achieve smoke-free pyrolysis operations.